|
ACS of Phosphating, Amination and Hydrazine of boiler BKZ 160–100 PT
Founded: October 2013 |
|
Contents
1 Object of automation
In exploitation of Kramatorskteploenergo Ltd is a Central Heat Energy (CHM) in contains of five working boilers BKZ 160–100 PT (5, 6, 7, 8 and 9). The boilers produce steam with pressure 100 kgf/cm2 and nominal productivity up to 160 ton/hour. Produced steam transferred to turbines and heat carrier of Kramatorsk city. As fuel of the boilers use the coal dust and the natural gas, mostly for ignition and light. The primary coal is non-gas (anthracite) coals which is less explosive and allow to milling on temperatures up to 150°С.
For supply of the boilers there uses addition and circulation water. The supply water needs for preparation previously for prevent scum formation and corrosion of the common and additive equipment. Same for correcting of the supply water applies of "Amination", "Hydrazine" and "Phosphating" (for boiler's water).
The corrosion decreasing performs by creation the reductive environment into the condensing tract and deep binding of oxygen and nitrite after deaerator through input Recovery, by regulation of рН value of the environment through input Ammonia. Higher grade of the binding of nitrite and residual oxygen can be doing by hydrazine-hydrate (in this case), hydrazine-sulphate, sodium-sulfate.
For prevent the scum formation the boiler's water processes by phosphates. Phosphating is effective way of preventing only to calcium scum formation. As part of the desalting process it is also continuous blowing of the boiler that is continuous flow of the salting water from the boiler's drum bottom. The continuous blowing also included to the ACS "Phosphating".
2 ACS
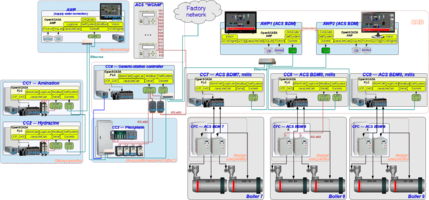
Structural scheme of the ACS shown on Figure 1, it is contains four cabinets of controllers and Automation Work Place (AWP) of operator.
ACS "Amination" and "Hydrazine" located into a single placement "Water-preparation", but them are implemented into different cabinets CC1 and CC2, accordingly. Into each of the cabinets placed an individual controller, and the controller of ACS "Hydrazine" connected to local network through second interface of the controller of ACS "Amination", where both of the interfaces connected to a "Bridge". Main aim of the ACS "Amination" and "Hydrazine" is dosing transfer of ammonia and hydrazine-hydrate to the supply water, which performs by pumps connected through Frequency Converters (FC). Control by the FC performs from the PLC by the link interface RS-485 and the protocol ModBus/RTU.
ACS "Phosphating" divided to two parts. First part is presented by cabinet CC4 (placement of Central Heat Board) and into it installed PLC, and second part is presented by cabinet CC3 (placement of nonoperative contour of boiler #8) with a tray of Object Adjustment Devices (OAD) and frequency converters of pumps of transferring phosphates to boilers #6,7,8,9. Common signals of ACS connected to the OAD tray which self connected to the PLC by the interface RS-485 and the protocol DCON. Control by the FC of transferring phosphates performs from PLC by the link interface RS-485 and the protocol ModBus/RTU. Connecting the PLC to the local network performs by a switch into the cabinet CC3, moreover the two pares of RS-485 and other two of Ethernet routed between the cabinets CC3 and CC4 by single cable of twist pairs of category 5 by length about 100m.
PLC CC4 (placement of Central Heat Board) besides the functions of the ACS "Phosphating" includes also functions of ACS "Continuous blowing" and ACS "Water Chemical Mode (WChM)", and why had it's naming as "Generic-station".
ACS "Continuous blowing", implemented into the generic-station controller, represented by valves of flow rate of continuous blowing with a pulse control. ACS signals entered direct to the PLC modules. Due to need of controlling the ACS by operator of the boilers it's interface entered to ACS BDM, and the Generic-station PLC enabled to network of ACS "BDM".
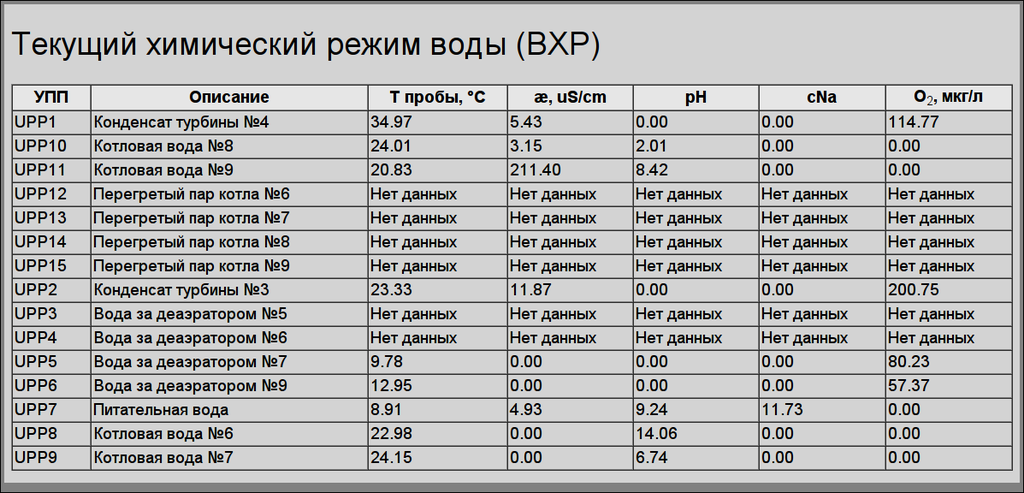
ACS "WchM" implemented base on devices of analysis the chemical water mode (UPP) from a previous system, which AWP (implemented on the closed technologies) in time was unworkable. That all this devices UPP (15 items), into the network RS-485 by protocol ModBus/RTU, were connected to the Generic-station PLC. Some parameters of the ACS used into ACS "Amination", "Hydrazine", "Phosphating" and "Continuous blowing" for control to transporting/dosing by the analysis. In generic each of the UPP allow to measure following parameters: "Temperature of the sample", "Value of pH", "Value of cNa", "Value of dissolved O2", "Electrolytic conductivity".
All the nodes of ACS connected to local network of ACS "Water", into an individual mask, which physically has enter to the factory network.
2.1 PLC
As a programmable logic controller in the project used PLC LP-8781 of ICP DAS company of LinPAC family. The industrial controller of this family is the first product built on the x86-compatible processor and it is free from low performance into float-point calculations of the environments based on ARM processors.
PLC (Fig. 2) is structurally made in a modular manner, where the modules are installed in the rack. Rack is combined with a processor module and can have 1, 3 or 7 slots for expansion modules. Expansion modules can be of two types, that is modules in parallel and serial bus. Modules on the parallel bus (I-8x) are fast. Modules on the serial bus (I-87x) are installed on the bus of RS-485 interface and operate at a speed of 115000 bps on the DCON protocol. In addition to modules directly into the rack the controller can be expanded with additional racks with modules on the serial bus (I-87x) through the serial interfaces of the processor. One the rack of extension I-87K9 (Fig.3) was been used for acquisition signals of ACS "Phosphating".
The controller's CPU has next technical characteristics:
| CPU | AMD LX800 processor (32-bit and 500 MHz) |
| System memory | 1 GB RAM |
| Dual Battery Backup SRAM | 512 KB (for 5 years data retain) |
| Flash | 4 GB as IDE Master |
| EEPROM | 16 KB Data Retention: 40 years; 1,000,000 erase/write cycles |
| CF Card | 8 GB (support up to 32 GB) |
| 64-bit Hardware Serial Number | Yes |
| Dual Watchdog Timer | Yes |
| VGA | 640 x 480 1024 x 768 |
| Ethernet Port | RJ-45 x 2, 10/100 Base-TX Ethernet Controller (Auto-negotiating, auto MDI/MDI-X, LED indicator) |
| USB 1.1 (host) | 2 |
| COM1 | Internal communication with I-87K modules in slots |
| COM2 | RS-232 (RxD, TxD and GND); Non-isolated |
| COM3 | RS-485 D2+,D2-;self-tuner ASIC inside Isolation 3000 VDC |
| COM4 | RS-232/RS-485 (RxD, TxD, CTS, RTS and GND forData- for RS-485); RS-232, Data+ and Data- for RS-485); Non-isolated |
| COM5 | RS-232 (RxD, TxD, CTS, RTS, DSR, DTR, CD, RI and GND); Non-isolated |
| Input Range | +10 VDC +30 VDC |
| Operating Temperature | -25 °C +75 °C |
The expansion rack I-87K{X} has next technical characteristics:
| COM2 | RS-485 (Data+, Data-); Voltage of isolation 3000V. |
| Power supply | Unregulated +10V ... +30V |
| Operating Temperature | -25 +75 °C |
Summary capacity of the САУ it is: 27AI, 115DI, 101DO. According to the structure the ACS built on three controllers and on rack of expansion which filling of modules is:
| Slot | Module | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| ACS Amination (CC1) | ||
| 1, 2, 3 | LP-8781 | Rack to 10 slots with the processor in slots 1-3 |
| 4 | I-87019RW | 8-channels AI. |
| 5 | I-87040W | 32 channels DI. |
| 6 | I-87041W | 32 channels DO. |
| 7 | Free | |
| 8 | Free | |
| 9 | Free | |
| 10 | Free | |
| ACS Hydrazine (CC2) | ||
| 1, 2, 3 | LP-8781 | Rack to 10 slots with the processor in slots 1-3 |
| 4 | I-87017ZW | 10-channels AI. |
| 5 | I-87040W | 32 channels DI. |
| 6 | I-87040W | 32 channels DI. |
| 7 | I-87041W | 32 channels DO. |
| 8 | I-87041W | 32 channels DO. |
| 9 | Free | |
| 10 | Free | |
| ACS Phosphating (CC3) | ||
| 1 | I-87K9 | Rack to 10 slots with the converter in slots 1 |
| 2 | I-87017ZW | 10-channels AI. |
| 3 | I-87017ZW | 10-channels AI. |
| 4 | I-87040W | 32 channels DI. |
| 5 | I-87041W | 32 channels DO. |
| 6 | Free | |
| 7 | Free | |
| 8 | Free | |
| 9 | Free | |
| 10 | Free | |
| Generic-station controller (CC4) | ||
| 1, 2, 3 | LP-8781 | Rack to 10 slots with the processor in slots 1-3 |
| 4 | I-87017ZW | 10-channels AI. |
| 5 | I-87040W | 32 channels DI. |
| 6 | I-87041W | 32 channels DO. |
| 7 | Free | |
| 8 | Free | |
| 9 | Free | |
| 10 | Free | |
For UPS connection used a USB interface of controller and AWP.
Firmware of the program environment created according to the instruction here.
In process of implementing, testing and exploiting OpenSCADA in role of an execution environment there were detected and fixed some problems, that is:
- DAQ.BlockCalc: not start or stop execution of a block scheme in case of an exception on write to RO attribute.
- DAQ.BlockCalc: not always correct sorting blocks into need sequence into it's obviously configuration.
- DAQ.ICP_DAS: unstable commands passing from controller CC4 due lack locking of the resource of selecting a slot of module into the PLC rack.
- DAQ.JavaLikeCalc: crashing in proceeds (compiling, executing, removing) of dynamic procedures of a parameters list into single object of the function.
2.2 AWP
Automation Work Place (AWP) of operator implemented in base of monoblock PC "Asus EeeTop PC ET1612" with a sensor screen and following configuration:
| Component | Naming |
|---|---|
| Processor | Intel Celeron 847 (1.1 ГГц), two core |
| Chipset | Intel HM70 |
| Operational memory | DDR3 2 Гб |
| Solid state drive (SSD) | Goodram Play 32GB 2.5" |
| Interfaces | 2 x RS232, RJ-45, 2 x USB 2.0, 2 x USB 3.0, WLAN |
| Multimedia | builtin dynamics 2х1.5 W; microphone; Web-camera; Card reader MMC/SD/SDHC |
| Keyboard | ASUS AK1D |
| Mouse manipulator | ASUS AM1D |
| Display | 15,6" / 1366x768 / Sensor |
The operator's AWP was set on a table into placement of laboratory, Figure 4.
At the AWP was installed the system software environment of ALTLinux T6 and the SCADA-system OpenSCADA 0.9-Work.
The following activities on the system-wide configuration were done, which were collected to an archive and transferred to the customer together with a disk of ACS "Water" project:
- The time synchronization was configured for controllers with AWP.
- An account of the operator "operator" with the password by default was created.
- An automatic loading of the working interface on behalf of the operator and the launch of the OpenSCADA with the ACS project was configured.
- TDE desktop environment is configured to eliminate unnecessary functions when working with dialog boxes and excluding the possibility of closure of the operator interface by the mouse.
In process of implementing, testing and exploiting OpenSCADA in role of SCADA-station was detected and fixed a problems list, that is:
- Archive.FSArch: not connecting of archive's files which source appears with a delay.
- Archive.FSArch: deformation of some archive's files with low quality, mostly in minutes, accompanied by loss a "error value" into it's end and in aftereffect it is error set of the parameter's archive top far to future, into physical end of the problematic archive.
- UI.Vision: unfit of the gradient filling of primitive "ElFigure".
3 User interface
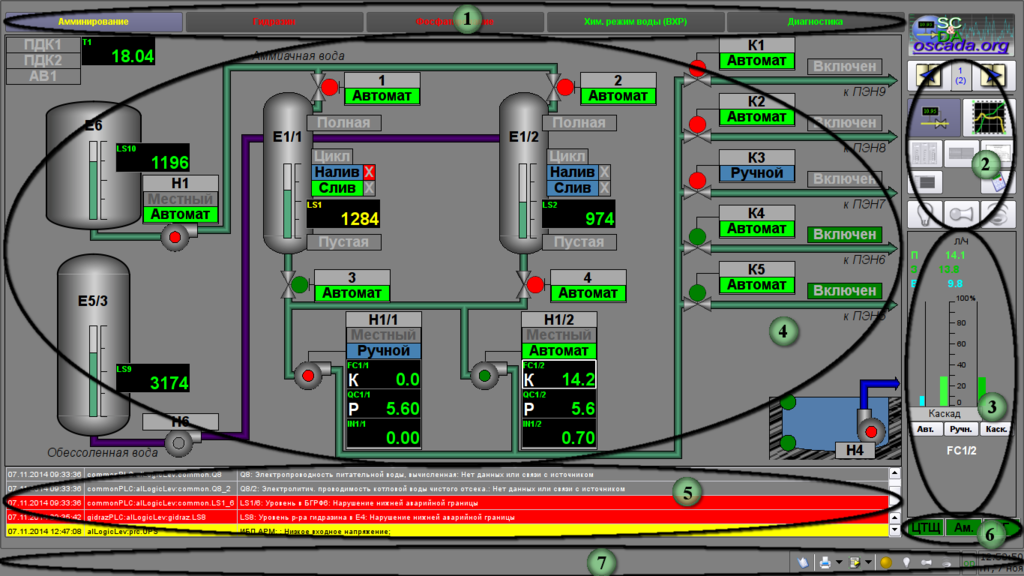
Information about the technological process represents on video-cadres forming by the program of displaying on a display's screen as part of AWP. The displaying information has a defined output area into the video-cadre and depends from it's destination. On figure 5 by digits is pointed the output areas of the video-cadre:
- 1. panel of signal objects;
- 2. panel of selection of displaying type, navigation by the video-cadres and local quittance;
- 3. panel of control;
- 4. workplace of the displaying;
- 5. active violation tables;
- 6. states of connections to PLC;
- 7. panel of states with instruments.
The controlling object divides in functions and technological to blocks which call as the signal objects. To each of the signal object assigns some grouped video-cadres set. The signal object represents set of screen's buttons for the objects and it's linked video-cadres' groups selection.
The signal object includes following buttons:
- "Amination" — group of video-cadres of control for amination of supply water.
- "Hydrazine" — group of video-cadres of control for transferring hydrazine-hydrate to the supply water.
- "Phosphating" — group of video-cadres of control for transferring phosphates to boiler's water.
- "WChM" — group of video-cadres of control by chemical mode of the water.
- "Diagnostic" — group of video-cadres of the automation equipment diagnostic.
To each of signal object can be linked next types of video-cadres:
- mnemonics;
- groups of graphic;
- groups of overview graphics;
- groups of parameter's contours;
- documents.
3.1 Mnemonics
The mnemonics window calls by pressing to proper button of the representing type and pointed to:
- graphical (mnemonically) representing of a frame of the control object;
- representing of current state of parameter into a graphical view;
- representing current state of parameter into a text view;
- call to a window of the parameter to the control panel.
3.1.1 Amination
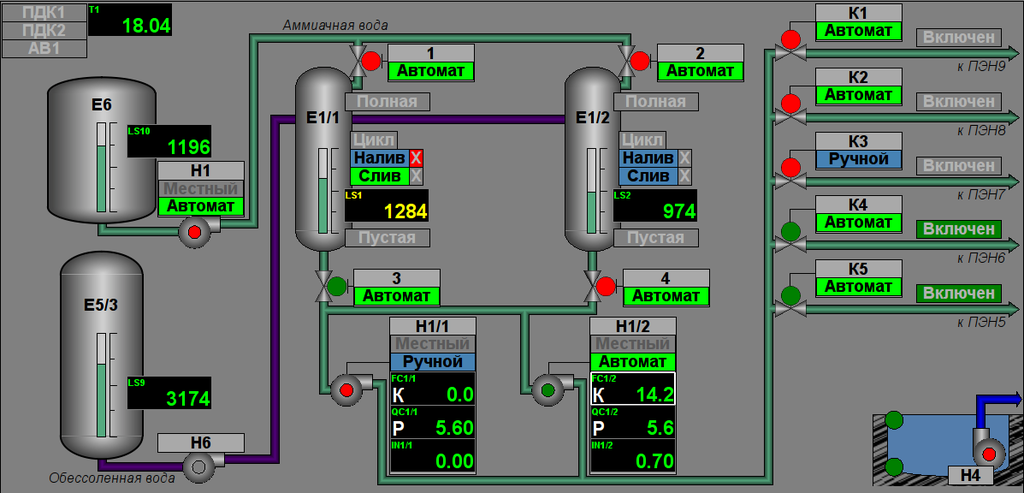
Controlling by the process of amination performs by two mnemonics, first one is "Main" (Fig.6) contained a mnemonic imagination of the technological process with elements of controlling, and second one is "Configuration of external regulation" (Fig. 7) contained configuration of external regulations, respectively.
3.1.2 Hydrazine
Controlling by the process of hydrazine performs by three mnemonics, first two are "Main" (Fig. 8 and 9) contained a mnemonic imagination of the technological process with elements of controlling, and third one is "Configuration of external regulation" (Fig. 10) contained configuration of external regulations, respectively.
3.1.3 Phosphating
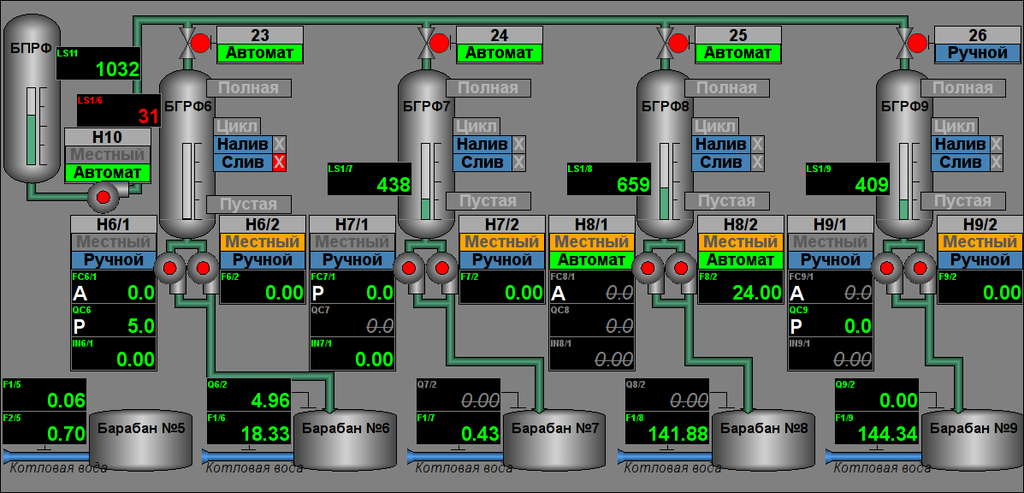
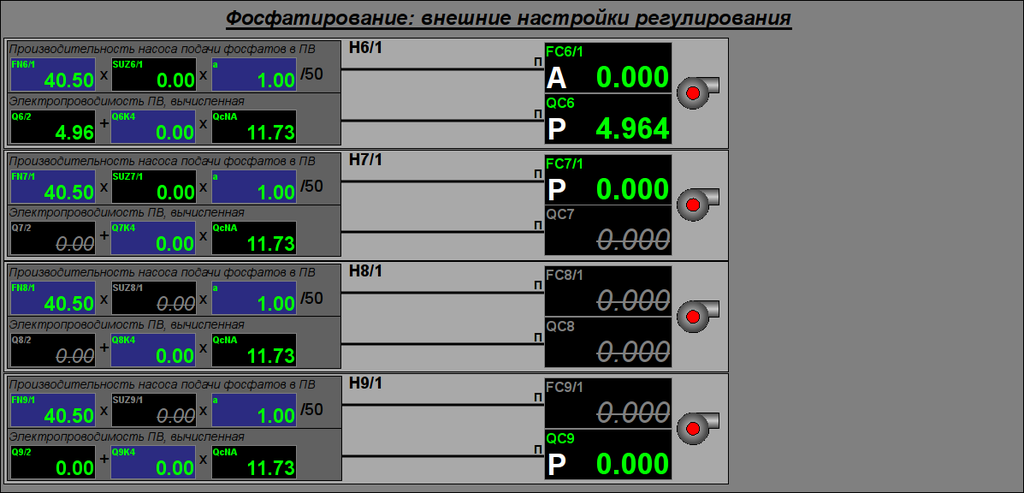
Controlling by the process of phosphating performs by two mnemonics, first one is "Main" (Fig.11) contained a mnemonic imagination of the technological process with elements of controlling, and second one is "Configuration of external regulation" (Fig. 12) contained configuration of external regulations, respectively.
3.1.4 Chemical water mode (WChM)
Controlling by the chemical water mode performs by one mnemonic with a result table of water's parameters (Fig. 13).
3.1.5 Diagnostic
Controlling by the equipment of the ACS performs by mnemonic "Main" (Fig. 14).
3.1.6 Continuous blowing
Controlling by process of the continuous blowing performs form AWP "Mills" by mnemonic "Main" (Fig.15).
3.2 Group of graphics of parameter's values
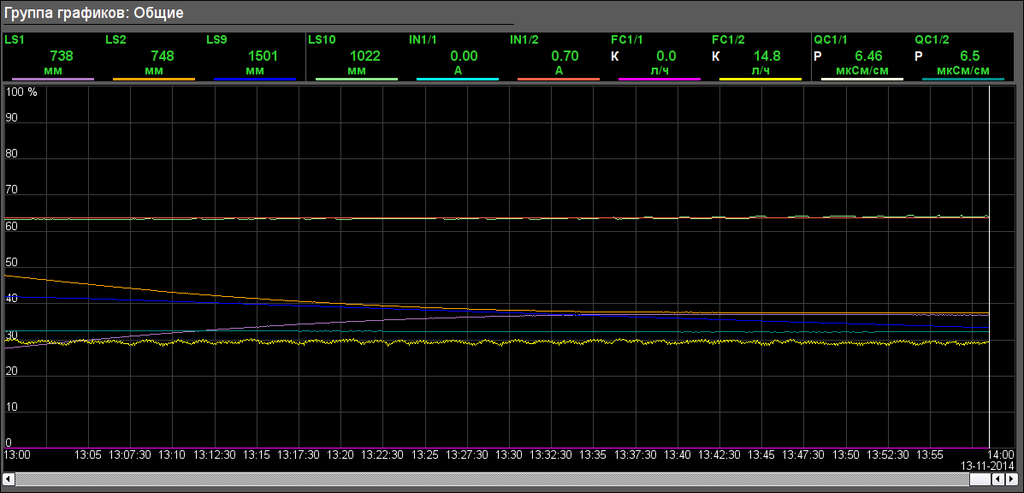
The window of group of graphics calls by pressing to proper button of the representing type and appointed for view of values up to ten parameters into graphical view for pointed time.
There provided twenty groups of graphics of technological parameters in next configuration per the signal objects:
- Amination: "Main" (Fig. 16)
- Hydrazine: "Main", "Environment"
- Phosphating: "Levels", "Pumps productivity", "Conductivity", "Pumps", "Supply water".
- Chemical water mode: "Supply water", "Turbines condensate", "Water for Deaerators", "Drum water К6,7", "Drum water К8,9", "Overheated steam of boiler К6,7", "Overheated steam of boiler К8,9".
- Continuous blow: "Blow flows", "Blows valves".
- Diagnostic: "AWP", "PLC: Generic-station", "PLC: Amination", "PLC: Hydrazine".
3.3 Documents
The documents window calls by pressing to proper button of the representing type and contains a document from a list of allowed.
3.3.1 Protocol of interruption
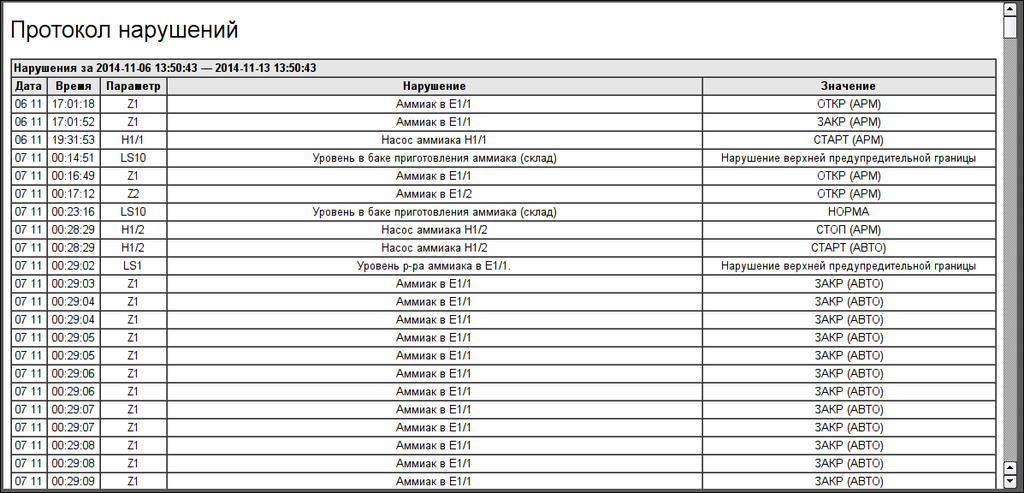
The protocol of interruption (Fig. 17) provides for overview of operator doings which performed from same AWP (changing of deblock keys stats, modes, configuration coefficients of regulators and other).
3.3.2 Protocol of violations
The protocol of violations (Fig. 18, 19, 20) provides for overview the violations in selected signal object (violation of order boards, inauthenticity, diagnostic of parameter and other).